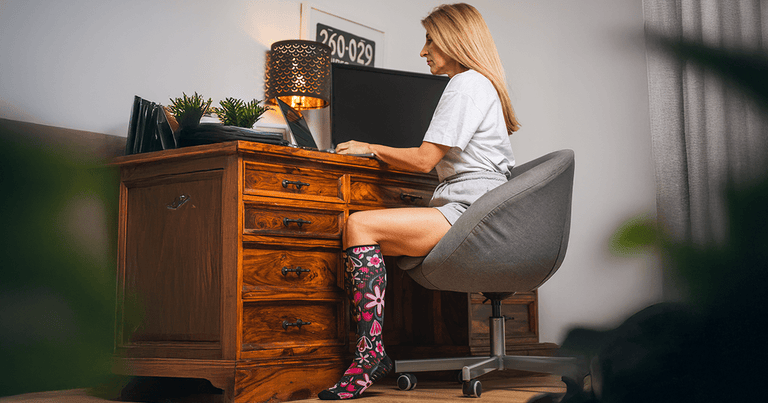
Whether standing for hours, running between meetings, or sitting at a desk all day, your feet and legs take a lot during the workday. Choosing the right pair of socks can make a surprising difference in how energized and comfortable you feel during work and after hours.
Viasox Blogs For People
How to Care for Compression & EasyStretch™ Socks to Make Them Last Longer

When you find socks you love—especially ones that offer the perfect blend of comfort, support, and style—you want them to last. At Viasox, we design Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks with premium materials to deliver lasting performance. But even the best socks need a little TLC.
Finding the Right Fit: What to Look for in Compression Socks & EasyStretch™ Socks

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures.
How to Style Your Compression Socks: Fashion Meets Function

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.
Socks and Compression Socks Fit into Your Routine

Finding the perfect pair of socks can be a game-changer in your daily comfort and overall well-being. At Viasox, we understand that every lifestyle demands different support and ease. We offer two standout products: EasyStretch™ Socks and Compression Socks. Each has distinct features to cater to your varied activities, whether at work, home, or constantly moving. This blog explores how these socks can seamlessly fit into your daily routine, elevating your comfort from morning until night.
What to Look for in Compression Socks & EasyStretch™ Socks

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures
How to Style Your Compression Socks: Fashion Meets Function

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.
Compression vs. EasyStretch™ Socks: Which One Is Right for You?

Choosing the right socks can significantly impact your daily comfort and overall foot health. At Viasox, we offer two distinct types of socks to cater to your needs: Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks. Understanding their differences will help you select the perfect pair for your lifestyle.
Compression Socks for Road Trips: How They Help During Long Car Rides
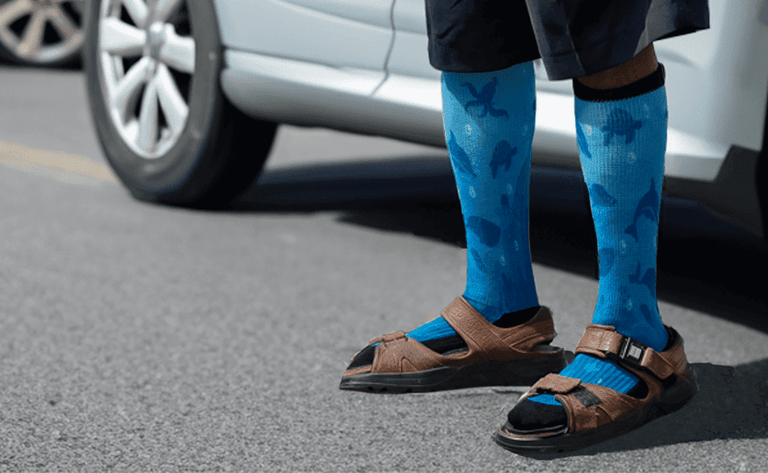

Road trips are an exciting way to explore new places, enjoy scenic drives, and create memorable experiences. However, the long hours spent sitting in a car can sometimes be less than ideal for your legs and feet. Whether you’re behind the wheel or a passenger, staying in one position for extended periods can lead to tired, stiff legs. Fortunately, there’s an easy and stylish solution: compression socks.
How To Put On A Compression Sock

Compression socks can be a game-changer for anyone looking to improve circulation, reduce swelling, or stay comfortable during long hours on their feet. However, putting them on can sometimes feel tricky, especially if you’re new to compression wear. To make the process easier and ensure you’re getting the maximum benefit, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to put on a compression sock correctly.
Best Compression Socks for Standing All Day: A Lifesaver for Teachers, Nurses, and Retail Workers
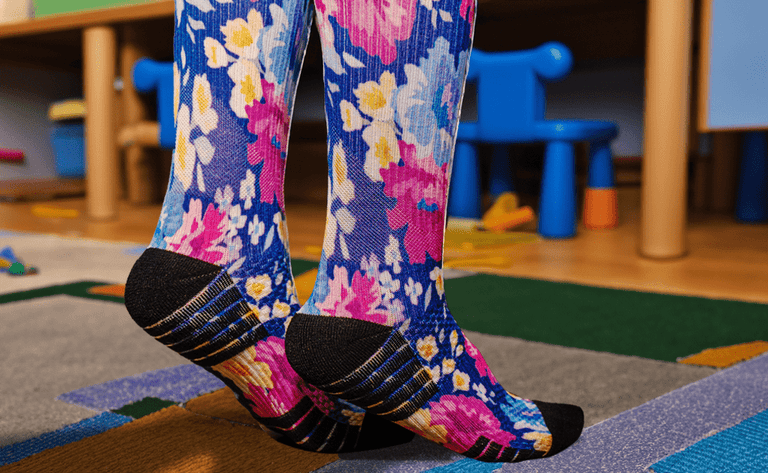
The holiday season is a busy time for everyone, but it’s especially challenging for professionals who spend long hours on their feet. Teachers juggle festive classroom activities, nurses provide essential care during busy hospital shifts, and retail workers assist endless lines of holiday shoppers. These demanding roles require stamina, focus, and energy—but they can also take a toll on your legs and feet. That’s where compression socks come in.
Compression Socks for Hiking: How They Can Help
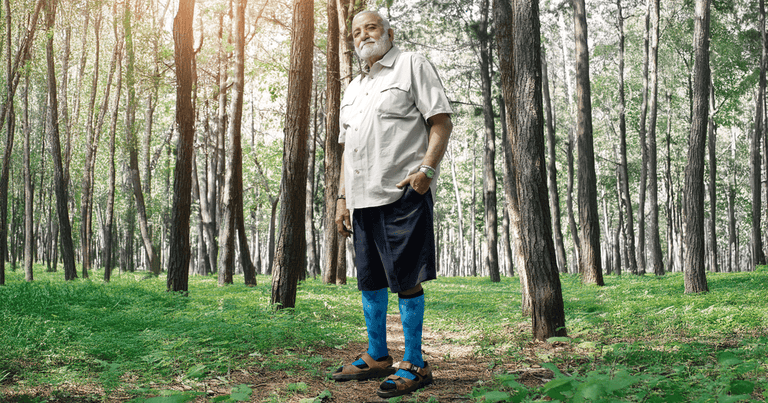

Hiking is one of the best ways to connect with nature, test your endurance, and experience breathtaking views. Whether you're tackling a short day hike or embarking on a multi-day trek, the physical demands of hiking can challenge your legs and feet. Uneven trails, steep inclines, and long hours on your feet can lead to fatigue, discomfort, and even impact your overall hiking performance. This is where compression socks come in. Designed to support your legs and reduce fatigue, compression socks are a game-changer for hikers looking to elevate their experience on the trails.
How to Care for Compression & EasyStretch™ Socks to Make Them Last Longer

When you find socks you love—especially ones that offer the perfect blend of comfort, support, and style—you want them to last. At Viasox, we design Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks with premium materials to deliver lasting performance. But even the best socks need a little TLC.

When you find socks you love—especially ones that offer the perfect blend of comfort, support, and style—you want them to last. At Viasox, we design Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks with premium materials to deliver lasting performance. But even the best socks need a little TLC.
Finding the Right Fit: What to Look for in Compression Socks & EasyStretch™ Socks

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures.

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures.
How to Style Your Compression Socks: Fashion Meets Function

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.
Socks and Compression Socks Fit into Your Routine

Finding the perfect pair of socks can be a game-changer in your daily comfort and overall well-being. At Viasox, we understand that every lifestyle demands different support and ease. We offer two standout products: EasyStretch™ Socks and Compression Socks. Each has distinct features to cater to your varied activities, whether at work, home, or constantly moving. This blog explores how these socks can seamlessly fit into your daily routine, elevating your comfort from morning until night.

Finding the perfect pair of socks can be a game-changer in your daily comfort and overall well-being. At Viasox, we understand that every lifestyle demands different support and ease. We offer two standout products: EasyStretch™ Socks and Compression Socks. Each has distinct features to cater to your varied activities, whether at work, home, or constantly moving. This blog explores how these socks can seamlessly fit into your daily routine, elevating your comfort from morning until night.
What to Look for in Compression Socks & EasyStretch™ Socks

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures

Choosing the perfect pair of socks can make all the difference in your daily comfort and overall performance. With options ranging from Compression Socks designed to energize your legs to EasyStretch™ Socks that provide unmatched everyday comfort, selecting the right pair hinges on several key factors. In this blog, we’ll dive into what to look for when choosing your next pair, focusing on material, sizing, pattern availability, and stretchability. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs, whether you're navigating busy workdays, home routines, or outdoor adventures
How to Style Your Compression Socks: Fashion Meets Function

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.

Compression socks have long been celebrated for their benefits in supporting circulation and reducing fatigue, but today’s Viasox compression socks bring a delightful twist to the table—fashion meets function. Gone are the days when compression socks were relegated to “medical wear.” Now, they're a statement piece that adds a pop of personality to your wardrobe while keeping you comfortable and supported all day. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out, a professional environment, or an adventure, here’s your fun guide to pairing compression socks with your favorite outfits.
Compression vs. EasyStretch™ Socks: Which One Is Right for You?

Choosing the right socks can significantly impact your daily comfort and overall foot health. At Viasox, we offer two distinct types of socks to cater to your needs: Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks. Understanding their differences will help you select the perfect pair for your lifestyle.

Choosing the right socks can significantly impact your daily comfort and overall foot health. At Viasox, we offer two distinct types of socks to cater to your needs: Compression Socks and EasyStretch™ Socks. Understanding their differences will help you select the perfect pair for your lifestyle.
Compression Socks for Road Trips: How They Help During Long Car Rides

Road trips are an exciting way to explore new places, enjoy scenic drives, and create memorable experiences. However, the long hours spent sitting in a car can sometimes be less than ideal for your legs and feet. Whether you’re behind the wheel or a passenger, staying in one position for extended periods can lead to tired, stiff legs. Fortunately, there’s an easy and stylish solution: compression socks.

Road trips are an exciting way to explore new places, enjoy scenic drives, and create memorable experiences. However, the long hours spent sitting in a car can sometimes be less than ideal for your legs and feet. Whether you’re behind the wheel or a passenger, staying in one position for extended periods can lead to tired, stiff legs. Fortunately, there’s an easy and stylish solution: compression socks.
How To Put On A Compression Sock

Compression socks can be a game-changer for anyone looking to improve circulation, reduce swelling, or stay comfortable during long hours on their feet. However, putting them on can sometimes feel tricky, especially if you’re new to compression wear. To make the process easier and ensure you’re getting the maximum benefit, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to put on a compression sock correctly.

Compression socks can be a game-changer for anyone looking to improve circulation, reduce swelling, or stay comfortable during long hours on their feet. However, putting them on can sometimes feel tricky, especially if you’re new to compression wear. To make the process easier and ensure you’re getting the maximum benefit, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to put on a compression sock correctly.
Best Compression Socks for Standing All Day: A Lifesaver for Teachers, Nurses, and Retail Workers
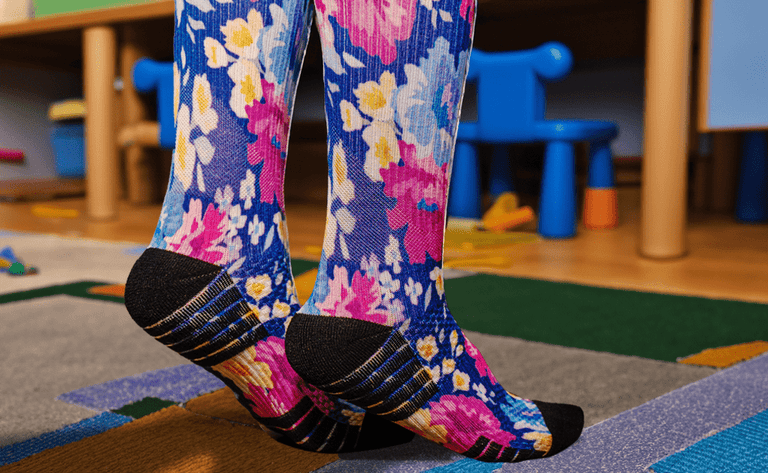
The holiday season is a busy time for everyone, but it’s especially challenging for professionals who spend long hours on their feet. Teachers juggle festive classroom activities, nurses provide essential care during busy hospital shifts, and retail workers assist endless lines of holiday shoppers. These demanding roles require stamina, focus, and energy—but they can also take a toll on your legs and feet. That’s where compression socks come in.
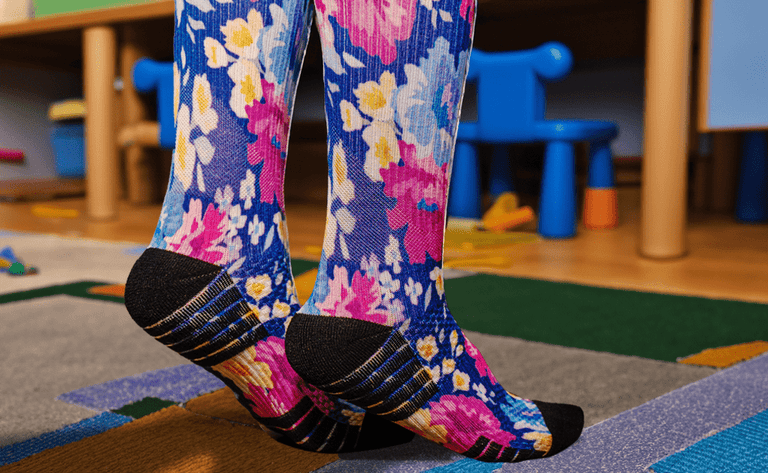
The holiday season is a busy time for everyone, but it’s especially challenging for professionals who spend long hours on their feet. Teachers juggle festive classroom activities, nurses provide essential care during busy hospital shifts, and retail workers assist endless lines of holiday shoppers. These demanding roles require stamina, focus, and energy—but they can also take a toll on your legs and feet. That’s where compression socks come in.
Compression Socks for Hiking: How They Can Help

Hiking is one of the best ways to connect with nature, test your endurance, and experience breathtaking views. Whether you're tackling a short day hike or embarking on a multi-day trek, the physical demands of hiking can challenge your legs and feet. Uneven trails, steep inclines, and long hours on your feet can lead to fatigue, discomfort, and even impact your overall hiking performance. This is where compression socks come in. Designed to support your legs and reduce fatigue, compression socks are a game-changer for hikers looking to elevate their experience on the trails.

Hiking is one of the best ways to connect with nature, test your endurance, and experience breathtaking views. Whether you're tackling a short day hike or embarking on a multi-day trek, the physical demands of hiking can challenge your legs and feet. Uneven trails, steep inclines, and long hours on your feet can lead to fatigue, discomfort, and even impact your overall hiking performance. This is where compression socks come in. Designed to support your legs and reduce fatigue, compression socks are a game-changer for hikers looking to elevate their experience on the trails.






















